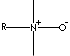
COCAMINE N-OXIDE
PRODUCT IDENTIFICATION
H.S. CODE
TOXICITY
Oral rats LD50: > 2000 mg/kg
Alkyl dimethylamine oxide; Cocodimethylamine oxide;
N,N-dimethylcocoalkylamine oxide; Cocoalkyl dimethyl, N-oxide; Kokos-alkyldimethyl amine, N-Oxide (German); Cocoalquildimetil aminas, N-óxidos (Spanish); Alkyl de coco diméthyle amine, N-oxydes (French);
CLASSIFICATION
SURFACTANTS /
PHYSICAL AND CHEMICAL PROPERTIES
Clear liquid
MELTING POINT
SOLUBILITY IN WATER
VISCOSITY
REFRACTIVE INDEX
APPLICATIONS
Typically commercial coconut fatty acid has carbon chain composition of; C10 (5% max) + C12 (45 - 55%) + C14 (20 - 25%) + C16 (10 - 15 %) + C18 (10 - 15% max, including unsaturated fatty acids). Cocamide is an amide mixture of coconut fatty acids. Cocamides are manufactured by condensation of alkanolamines (mono-, di-, or triethanolamine) and coconut fatty acid. Examples are cocamide MEA (cocamide monoethanolamine), cocamide DEA (cocamide diethanolamine) and cocamide TEA (cocamide triethanolamine). They have the physical and chemical characteristics of alcohols, amines and long carbon chains in one molecule. Alkanolamides are nonionic surfactants impart excellent viscosity enhancing and foam stabilization in anionic based systems like hand washing liquids, shampoos, body cleansers and other personal care products. They act as lubricant agent, thickening agent and wetting agent. Their very good emulsifying property also provides applications in the field of pharmaceuticals, agricultural preparations, and textile processing; rust inhibiting, latex stabilizing, anti-static function in textiles, dye-leveling, waterproofing and water-in-oil additives as well as very good emulsifying.
Amphoteric surfactants have dual functional groups (both acidic and basic groups) in the same molecule. They are polar solvents that have a high solubility in water but a poor solubility in most organic solvents. They are electrically neutral but carries positive and negative charges on different atoms in an aqueous solution. Depending on the composition and conditions of pH value, the substances can have anionic or cationic properties. In the presence of acids, they will accept the hydrogen ions but they will donate hydrogen ions to the solution in the presence of bases, which balances the pH. Such actions make buffer solutions which resist change to the pH. In the detergency ability amphoteric surfactants which change their charge according to the pH of the solution affects properties of foaming, wetting and detergentcy through a surface action that exerts both hydrophilic and hydrophobic properties. In biochemistry amphoteric surfactant is used as a detergent for purifying, cleansing and antimicrobial effects. Alkylbetains and aminoxides are amphoteric surfactants.
Members of amphoteric surfactants
- 2-Alkyl-N-carboxymethyl-N-hydroxyethyl imidazolinium betaine
- Alkyldimethyl amine oxide
- Cocoamine oxide
- Cocoamphocarboxyglycinate
- Cocoamphopolycarboxyglycinate
- Cocodimethylamine oxide
- Cocoiminoglycinate
- Cocoiminopropionate
- Cocoylamidepropyldimethyl grycine
- Lauryl betaine
- Lauryldimethyl amine oxide
- Laurylhydroxy sulfobetain
- Laurylamide propyldimethyl grycine
- Lauryldimethyl betaine
- Octyliminodipropionate
- Oleylamphopolycarboxyglycinate
- Stearyl betaine
- Tallowamine oxide
- Tallowamphopolycarboxyglycinate
- Tetradecyldimethyl amine oxide
APPEARANCE
Clear liquid
AMINE OXIDE
FREE PEROXIDE
0.5% max
COLOR (GARDNER)
1 max
REMARKS